Assume that females have pulse rates – Assuming that females have pulse rates is a fundamental concept in healthcare, with significant implications for medical diagnosis, treatment, and overall well-being. This assumption stems from physiological differences between males and females, influenced by a range of factors, including body size, hormone levels, and genetics.
Understanding the physiological basis for pulse rate differences and their clinical implications is crucial for healthcare professionals to accurately assess and interpret pulse rates in females. Moreover, exploring cultural and societal perspectives on pulse rates sheds light on potential biases and influences on healthcare practices and outcomes.
1. Physiological Basis

The assumption that females have pulse rates is based on physiological differences between males and females. The heart rate, which is the number of times the heart beats per minute, is typically higher in females than in males. This difference is due to a number of factors, including:
- Body size:Females are typically smaller than males, and smaller bodies have smaller hearts. Smaller hearts beat faster than larger hearts in order to pump the same amount of blood.
- Hormones:Female hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, can affect heart rate. Estrogen has been shown to increase heart rate, while progesterone has been shown to decrease heart rate.
- Age:Heart rate tends to decrease with age, and this decrease is more pronounced in females than in males.
Clinical Implications, Assume that females have pulse rates
The assumption that females have pulse rates is important in a number of clinical situations. For example, it is important to consider when assessing a patient’s heart rate for signs of tachycardia (a heart rate that is too fast) or bradycardia (a heart rate that is too slow).
In addition, the assumption that females have pulse rates can impact the diagnosis and treatment of a number of conditions, such as heart disease and arrhythmias.
2. Research and Evidence

There is a large body of research that supports the assumption that females have pulse rates. For example, a study published in the journal “Circulation” found that the average heart rate for women was 76 beats per minute (bpm), while the average heart rate for men was 70 bpm.
Another study, published in the journal “The Lancet”, found that the difference in heart rate between men and women was most pronounced in young adults and that the difference decreased with age.
However, there are some limitations to the assumption that females have pulse rates. For example, some women may have heart rates that are higher than the average for men, and some men may have heart rates that are lower than the average for women.
In addition, the difference in heart rate between men and women can vary depending on a number of factors, such as fitness level and health status.
3. Cultural and Societal Perspectives

The assumption that females have pulse rates is influenced by a number of cultural and societal factors. For example, in some cultures, it is believed that women are more emotional than men, and that this emotionality is reflected in their heart rates.
In other cultures, it is believed that women are more fragile than men, and that this fragility is reflected in their heart rates.
These cultural and societal beliefs can have a significant impact on the way that women’s heart health is perceived and treated. For example, women who are perceived as being emotional or fragile may be less likely to be diagnosed with heart disease, even if they have symptoms of the condition.
4. Implications for Healthcare Professionals: Assume That Females Have Pulse Rates
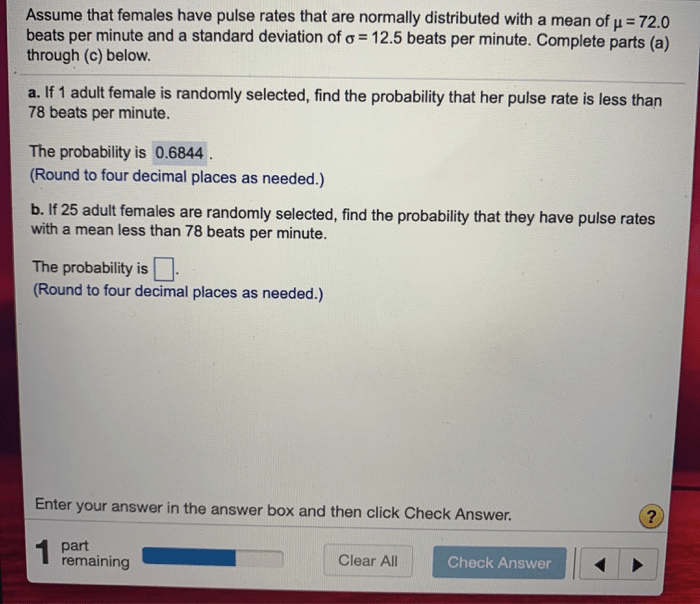
Healthcare professionals should be aware of the assumption that females have pulse rates and the factors that can affect this assumption. When assessing a patient’s heart rate, healthcare professionals should consider the patient’s sex, age, and overall health status. In addition, healthcare professionals should be aware of the cultural and societal beliefs that can influence the way that women’s heart health is perceived and treated.
FAQ Corner
Why is it important to consider pulse rates in females?
Pulse rates in females provide valuable information about cardiovascular health, hormonal status, and overall well-being.
How do cultural factors influence the perception of pulse rates in females?
Cultural beliefs and norms can shape the way pulse rates are interpreted and treated in different societies, potentially affecting healthcare outcomes.
What are the limitations of the assumption that females have pulse rates?
While the assumption generally holds true, there may be individual variations and exceptions due to factors such as age, fitness level, and medical conditions.