Section 12.1 discovering earth’s history – Section 12.1: Discovering Earth’s History embarks on an extraordinary journey to uncover the hidden chapters of our planet’s past. From the formation of rocks to the evolution of life, and the dynamic forces that have shaped our world, this exploration unveils the captivating narrative of Earth’s history.
Through the meticulous examination of geological formations, fossil records, and the intricate workings of plate tectonics, scientists have pieced together a comprehensive timeline of Earth’s existence. This knowledge empowers us to understand our place in the vastness of time and the interconnectedness of all living things.
Discovering Earth’s History: An Overview
Understanding Earth’s history is crucial for comprehending our planet’s present state and predicting its future. It provides insights into the formation of our solar system, the evolution of life, and the dynamic processes that have shaped our planet over billions of years.
Scientists employ various methods to investigate Earth’s past, including studying the rock record, examining fossils, analyzing plate tectonics, and monitoring climate change. These approaches provide valuable evidence that helps us piece together the complex tapestry of Earth’s history.
The Rock Record: A Window to the Past
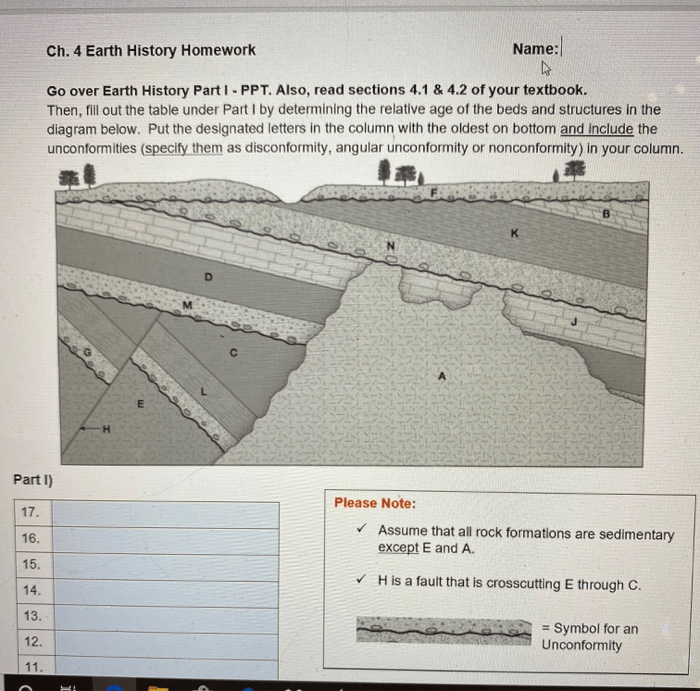
The rock record is a valuable source of information about Earth’s history. Sedimentary rocks, formed from the accumulation and cementation of sediments, contain clues about past environments and the presence of life. Igneous rocks, formed from the cooling and solidification of molten rock, provide insights into Earth’s internal processes and the composition of the mantle.
Metamorphic rocks, formed from the alteration of existing rocks under intense heat and pressure, reveal evidence of tectonic activity and the transformation of Earth’s crust.
Fossils: Evidence of Life’s Evolution, Section 12.1 discovering earth’s history
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of ancient organisms. They provide direct evidence of the history of life on Earth and the evolution of different species.
Paleontologists study fossils to reconstruct past ecosystems, trace the lineage of species, and understand the environmental changes that have influenced the evolution of life.
Plate Tectonics: Shaping Earth’s Surface
Plate tectonics is the theory that Earth’s crust is divided into large, rigid plates that move relative to each other. This movement is driven by convection currents in the Earth’s mantle and has shaped Earth’s surface features.
Plate tectonics has created mountains, oceans, and volcanoes and has played a significant role in the distribution of life on Earth.
Climate Change: Earth’s Dynamic Environment
Earth’s climate has undergone significant changes throughout its history. Factors such as solar radiation, volcanic eruptions, and the movement of tectonic plates have influenced these changes.
Scientists study past climate changes to understand the potential impacts of future climate change and develop strategies to mitigate its effects.
FAQ Compilation: Section 12.1 Discovering Earth’s History
What is the significance of studying Earth’s history?
Understanding Earth’s history provides valuable insights into the planet’s geological processes, the evolution of life, and the forces that have shaped our environment. It helps us comprehend the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems and make informed decisions for sustainable development.
How do scientists investigate Earth’s past?
Scientists utilize various methods to study Earth’s history, including examining rock formations, analyzing fossils, and studying the movement of tectonic plates. These techniques provide valuable clues about past geological events, climate conditions, and the evolution of life.
What are the different types of rocks and how do they provide evidence of Earth’s history?
Rocks are classified into three main types: sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic. Each type forms under distinct geological processes and contains unique characteristics that reveal information about past environments and events. Sedimentary rocks, for example, provide a record of ancient climates and depositional processes, while igneous rocks offer insights into volcanic activity and the formation of mountain ranges.