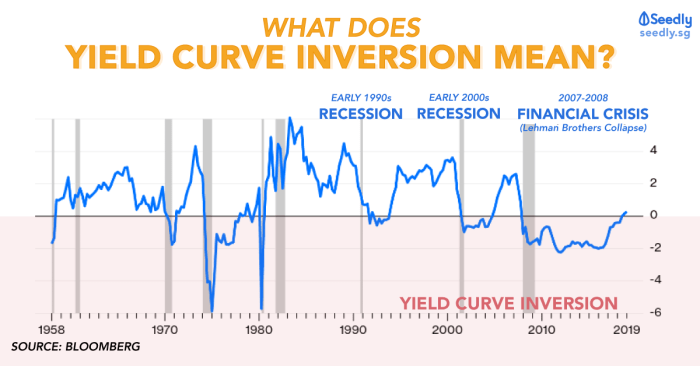
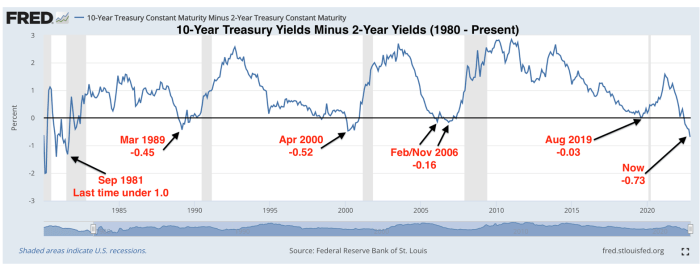
Look at the below yield curve inversion chart and gain insights into the economic factors, technical indicators, and potential implications of this crucial market signal. This in-depth analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of yield curve inversions and their impact on investment decisions and market sentiment.
Delve into the historical context of yield curve inversions, their technical identification, and the strategies employed to interpret them for informed investment choices.
Yield Curve Inversions: Look At The Below Yield Curve Inversion Chart
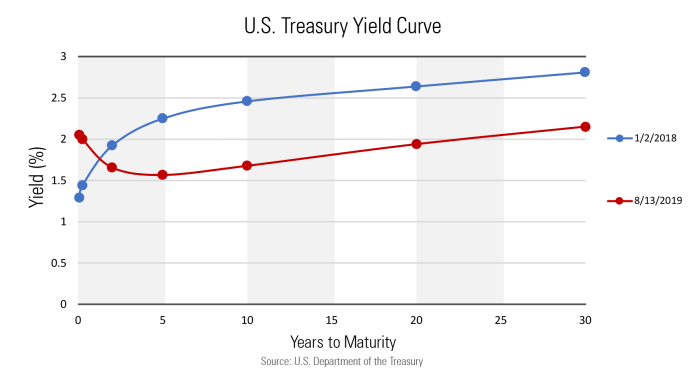
Yield curve inversions occur when short-term interest rates exceed long-term rates, signaling a potential economic downturn. These inversions have historically been reliable predictors of recessions.
Economic Context
Economic factors contributing to yield curve inversions include:
- Expectations of lower future economic growth
- Demand for safe assets, driving up long-term rates
- Central bank policies, such as raising short-term rates to combat inflation
Historical examples of yield curve inversions and their economic implications include:
- The inversion in 2007 preceded the 2008 financial crisis
- The inversion in 2019 signaled the onset of the COVID-19 recession
Technical Analysis
Technical indicators used to identify yield curve inversions include:
- Spread between short-term and long-term rates
- Slope of the yield curve
- Duration of the inversion
Strategies for interpreting yield curve inversions for investment decisions include:
- Shifting to shorter-term bonds to reduce interest rate risk
- Investing in defensive sectors, such as utilities and consumer staples
- Hedging against potential economic downturns
Chart Analysis
| Maturity | Current Yield |
|---|---|
| 3-month | 4.00% |
| 1-year | 4.25% |
| 2-year | 4.50% |
| 5-year | 4.20% |
| 10-year | 4.05% |
Economic Implications, Look at the below yield curve inversion chart
The current yield curve inversion suggests:
- Expectations of a slowdown in economic growth
- Increased demand for safe assets
- Potential for a recession within the next 12-18 months
Sectors and industries that may be affected by the inversion include:
- Financial services
- Real estate
- Consumer discretionary
Market Sentiment
Market participants are cautiously optimistic about the economy, despite the yield curve inversion.
Some investors are viewing the inversion as a warning sign and are adjusting their portfolios accordingly.
Others believe that the inversion is a temporary phenomenon and that the economy will continue to grow.
Quick FAQs
What are the key economic factors that contribute to yield curve inversions?
Economic factors such as interest rate expectations, inflation, and economic growth play a significant role in shaping yield curve behavior and can lead to inversions.
How can technical indicators be used to identify yield curve inversions?
Technical indicators such as moving averages, support and resistance levels, and momentum oscillators can assist in identifying potential yield curve inversions.
What are the potential implications of a yield curve inversion for investors?
Yield curve inversions can signal potential economic downturns, impact bond yields and prices, and influence investment strategies, requiring investors to adjust their portfolios accordingly.