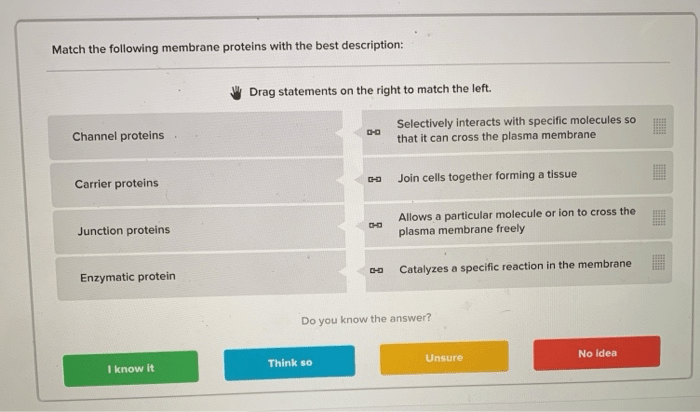
Match the following membrane proteins with the best description – Membrane proteins play a critical role in cellular processes, serving as gatekeepers for molecules entering and exiting the cell. Understanding their structure, function, and regulation is essential for comprehending cellular physiology and developing therapeutic interventions. This article provides a comprehensive overview of membrane proteins, their functions, interactions, regulation, and applications in biotechnology and medicine.
Membrane Protein Functions
Membrane proteins play a crucial role in cellular processes by facilitating the transport of molecules across the cell membrane, which is impermeable to most substances. They also participate in signal transduction, cell adhesion, and cell recognition.
Examples of membrane proteins include:
- Ion channels: Allow ions to flow across the membrane, maintaining electrochemical gradients and regulating cell excitability.
- Transporters: Move molecules against their concentration gradient, using energy from ATP or ion gradients.
- Receptors: Bind to specific ligands and initiate intracellular signaling cascades.
Membrane Protein Structure: Match The Following Membrane Proteins With The Best Description
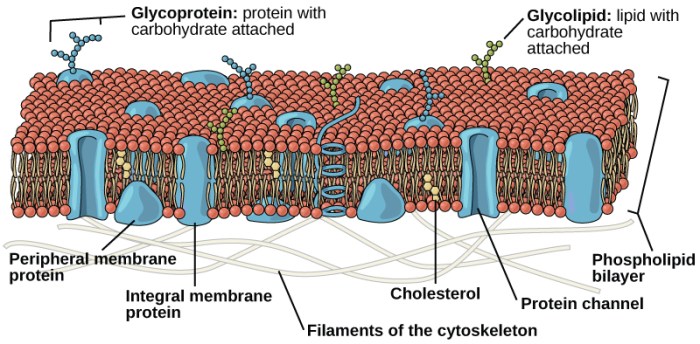
Membrane proteins are typically composed of a hydrophobic transmembrane domain that spans the lipid bilayer and hydrophilic domains that interact with the aqueous environment on either side of the membrane.
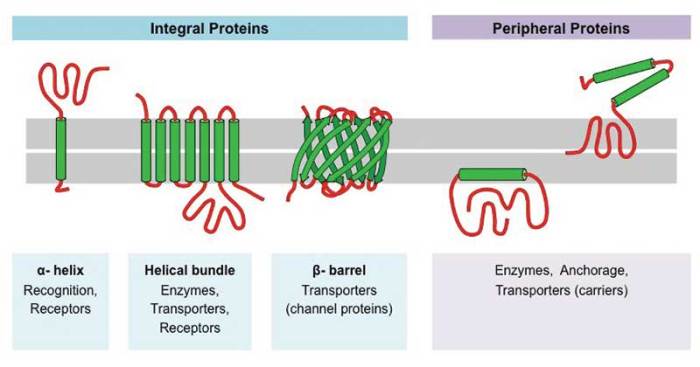
Based on their structure, membrane proteins can be classified as:
- Single-pass membrane proteins: Have a single transmembrane domain.
- Multi-pass membrane proteins: Have multiple transmembrane domains.
- Lipid-anchored membrane proteins: Attached to the membrane by a lipid anchor, such as a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor.
Membrane Protein Interactions
Membrane proteins interact with other molecules to perform their functions. These interactions include:
Protein-Protein Interactions, Match the following membrane proteins with the best description
Membrane proteins can interact with other membrane proteins, forming protein complexes that regulate membrane dynamics and function. For example, ion channels often form complexes with auxiliary subunits that modulate their activity.
Protein-Lipid Interactions
Membrane proteins interact with the surrounding lipid bilayer, which influences their structure and function. For example, the lipid environment can affect the conformation of transmembrane domains and the binding affinity of receptors.
Membrane Protein Regulation
Membrane proteins are regulated by various mechanisms, including:
Post-Translational Modifications
Membrane proteins can undergo post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation, glycosylation, and ubiquitination, which alter their activity and localization.
Signaling Pathways
Membrane proteins can be regulated by signaling pathways that activate or inhibit their activity. For example, the binding of a ligand to a receptor can trigger a signaling cascade that results in the phosphorylation of the receptor and modulation of its function.
Membrane Protein Techniques
Studying membrane proteins poses challenges due to their hydrophobic nature and complex structure. Techniques used to study membrane proteins include:
- X-ray crystallography: Determines the three-dimensional structure of membrane proteins.
- Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy: Provides information about the structure and dynamics of membrane proteins in solution.
- Electrophysiology: Measures the electrical activity of membrane proteins, such as ion channels and transporters.
Membrane Protein Applications
Membrane proteins have important applications in biotechnology and medicine:
Drug Development
Membrane proteins are targets for many drugs, including ion channel blockers, antipsychotics, and antibiotics.
Diagnostics
Membrane proteins are used in diagnostic tests to detect diseases, such as cancer and genetic disorders.
Questions and Answers
What are the main functions of membrane proteins?
Membrane proteins facilitate the transport of molecules across membranes, mediate signal transduction, and contribute to cell adhesion and recognition.
How are membrane proteins regulated?
Membrane proteins are regulated through various mechanisms, including post-translational modifications, protein-protein interactions, and signaling pathways.
What are the applications of membrane proteins in biotechnology and medicine?
Membrane proteins are targets for drug development and diagnostics, enabling the treatment and diagnosis of various diseases.